| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
A constant holds a value that does not change.
A constant declaration specifies the name, data type, and value of the constant and allocates storage for it. The declaration can also impose the NOT NULL constraint.
Topics:
Syntax
constant_declaration ::=

See expression ::=.
datatype ::=
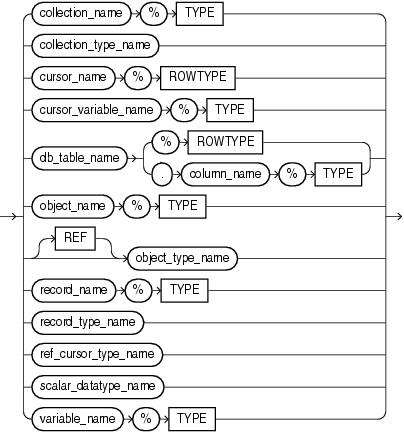
Semantics
collection_name
The name of a collection.
collection_type_name
A user-defined collection type defined using the data type specifier TABLE or VARRAY.
constant_name
The name of the constant that you are declaring.
cursor_name
The name of an explicit cursor.
cursor_variable_name
The name of a PL/SQL cursor variable.
db_table_name
The name of a database table or view, which must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
column_name
The name of a column in db_table_name.
expression
An expression whose value has a data type compatible with datatype (see Table 3-10, "Possible Implicit PL/SQL Data Type Conversions"). When constant_declaration is elaborated, the value of expression is assigned to constant_name. This value is the initial value of the constant.
NOT NULL
Prevents the program from assigning the value NULL to the constant.
PL/SQL subtypes NATURALN, POSITIVEN, and SIMPLE_INTEGER are predefined as NOT NULL. When declaring a constant of one of these subtypes, you can omit NOT NULL.
If you declare a NOT NULL constant, either by specifying NOT NULL or by specifying a subtype that is predefined as NOT NULL, you must also specify an initial value for the constant (see expression).
object_name
The name of an instance of a type.
record_name
The name of a record.
field_name
The name of a field of record_name.
record_type_name
The name of a user-defined type that was defined with the data type specifier RECORD.
ref_cursor_type_name
The name of a user-defined type that was defined with the data type specifier REF CURSOR.
%ROWTYPE
See "%ROWTYPE Attribute".
scalar_datatype_name
The name of a predefined scalar data type, including any qualifiers for size, precision, and character or byte semantics. For information about predefined scalar data types, see "Predefined PL/SQL Scalar Data Types and Subtypes".
%TYPE
See "%TYPE Attribute".
Examples
Related Topics
In this chapter:
In other chapters: