| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
An exception handler processes a raised exception (run-time error or warning condition). The exception can be either predefined or user-defined. The run-time system raises predefined exceptions automatically, but you must raise user-defined exceptions explicitly with either a RAISE statement or the procedure DBMS_STANDARD.RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR. The latter lets you associate an error message with the user-defined exception.
Topics:
Syntax
exception_handler ::=
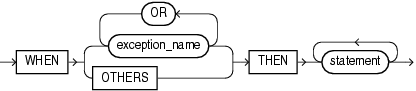
See statement ::=.
Semantics
exception_name
The name of either a predefined exception (see Table 11-2) or a user-defined exception (see "Exception").
If a specified exception is raised, the associated statement runs.
OTHERS
Specifies all exceptions not explicitly named in the exception-handling part of the block. WHEN OTHERS is optional. If used, it must be the last exception handler in the exception-handling part of the block.
If an exception that is not explicitly named is raised, the associated statement runs.
Examples
Example 7-13, "Validation Checks Guarding Against SQL Injection"
Example 8-1, "Declaring, Defining, and Invoking a Simple PL/SQL Procedure"
Related Topics
In this chapter:
In other chapters: