| Oracle® Database 2 Day + Application Express Developer's Guide Release 3.2 Part Number E11946-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database 2 Day + Application Express Developer's Guide Release 3.2 Part Number E11946-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This section describes Oracle Application Express, its architecture, and the environment for using the product. It also introduces you to concepts and terms used in this guide when discussing Oracle Application Express.
This section contains the following topics:
Oracle Application Express is a rapid Web application development tool for the Oracle database. Using only a Web browser and limited programming experience, you can develop professional applications that are both fast and secure. Thanks to built-in features such as user interface themes, navigational controls, form handlers, and flexible reports, Oracle Application Express accelerates the application development process.
From the end user's perspective, the deployed applications require only a browser and access to an Oracle database running Application Express.
Note:
This guide describes only a subset of Application Express functionality. For a complete list of features, see "What is Application Express?" in Oracle Application Express Application Builder User's Guide.Oracle Application Express installs with your Oracle database and is comprised of data in tables and PL/SQL code.
Whether you run the Oracle Application Express development environment or an application you built using Oracle Application Express, the process is the same. Your browser sends a URL request that is translated into the appropriate Oracle Application Express PL/SQL call. After the database processes the PL/SQL, the results are relayed back to your browser as HTML. This cycle happens each time you request or submit a page.
The application session state is managed in the database tables within Oracle Application Express. It does not use a dedicated database connection. Instead, each request is made through a separate database session, consuming minimal CPU resources.
About Oracle HTTP Server (Apache) and the Embedded PL/SQL Gateway
The version of Oracle Database you use determines how the URL is translated:
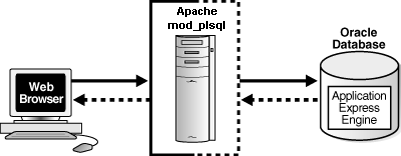
Versions before Oracle Database 11.1 require Oracle HTTP Server (Apache) with mod_plsql. The following illustration shows that architecture.
With Oracle Database 11.1 or later or Oracle Database 10g Express Edition, you can remove Oracle HTTP Server (Apache) from the architecture and replace it with the embedded PL/SQL gateway. The following illustration shows the architecture using the embedded PL/SQL gateway.
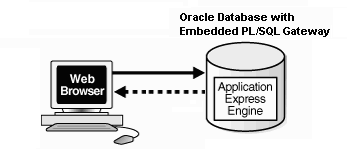
The embedded PL/SQL gateway provides Oracle Database with a Web server and also the necessary infrastructure to create dynamic applications. The embedded PL/SQL gateway runs in the XML DB HTTP server in the Oracle database and includes the core features of mod_plsql, but does not require the Oracle HTTP Server powered by Apache. Inclusion of the embedded PL/SQL gateway simplifies the architecture and eliminates the middle tier.
About the Application Express Engine
The Application Express engine renders and processes pages. It also performs these tasks:
Session state management
Authentication services
Authorization services
Page flow control
Validations processing
Oracle Application Express enables a single Oracle database to become a shared workgroup database service. Multiple users can access it using a Web browser without installing additional software.
The area where you develop applications is called a workspace. A workspace is a virtual private database that enables multiple users to work within the same Oracle Application Express installation while keeping their objects, data, and applications private.
In a typical development environment, you might create a single workspace for all your developers to share. However, you can also create dedicated workspaces for specific developers or projects. Creating a dedicated workspace limits access to the workspace objects to only those users associated with the workspace.
The following illustration shows the relationship among users and developers, workspaces, and database schemas.
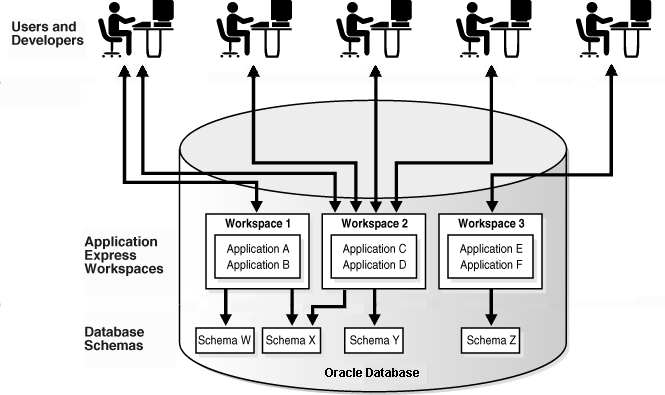
When you create a workspace, you associate it with a new or existing schema. A schema is a logical container for database objects such as tables, views, and stored procedures. A single schema can be associated with one or more workspaces.
When setting up Application Express users at a large organization, you assign roles and privileges to specific users. The roles within Oracle Application Express include the following:
Workspace administrators are users who perform administrator tasks specific to a workspace such as managing user accounts, monitoring workspace activity, and viewing log files. For this guide, you are acting as the workspace administrator when setting up the development environment.
Developers are users who create and edit applications. Developers can have their own workspace or share a workspace.
End users have no development privileges. You define end users so that they can access applications that do not use an external authentication scheme.
Oracle Application Express administrators are superusers that manage an entire hosted instance using the Application Express Administration Services application.
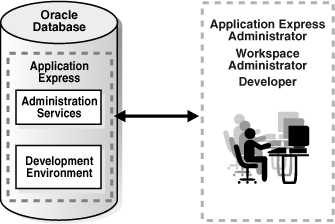
The following illustration shows multiple users with various roles accessing the Oracle Application Express development environment, Application Express Administration Services, and the published applications.
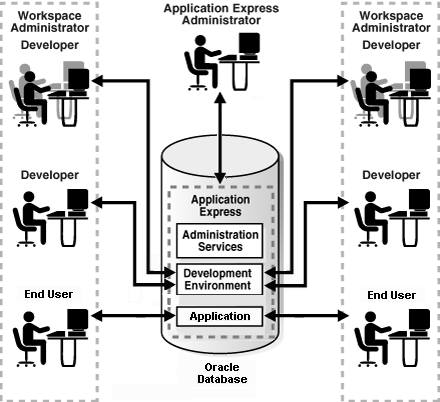
For this guide, you must have the privileges usually associated with three roles: Application Express Administrator, Workspace Administrator, and Developer. The following illustration shows an Oracle Application Express instance with a single user.
In "Building Your Application", you create a simple Human Resources (HR) application for a fictitious company called AnyCo Corp. The application manages departmental and employee information stored in the department and employees tables that you create. The tutorial shows you how to build the application, modify it, and then preview it.