| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10592-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10592-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
Syntax
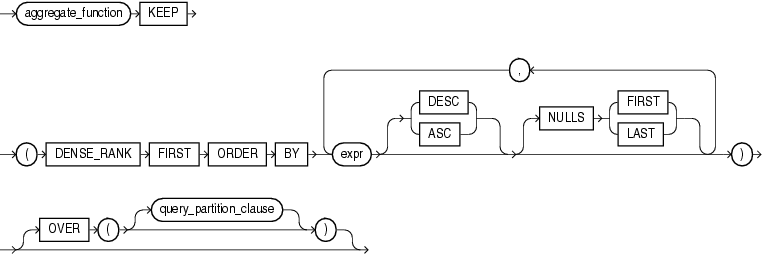
first::=
See Also:
"Analytic Functions" for information on syntax, semantics, and restrictions of theORDER BY clause and OVER clausePurpose
FIRST and LAST are very similar functions. Both are aggregate and analytic functions that operate on a set of values from a set of rows that rank as the FIRST or LAST with respect to a given sorting specification. If only one row ranks as FIRST or LAST, then the aggregate operates on the set with only one element.
If you omit the OVER clause, then the FIRST and LAST functions are treated as aggregate functions. You can use these functions as analytic functions by specifying the OVER clause. The query_partition_clause is the only part of the OVER clause valid with these functions. If you include the OVER clause but omit the query_partition_clause, then the function is treated as an analytic function, but the window defined for analysis is the entire table.
These functions take as an argument any numeric data type or any nonnumeric data type that can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type. The function returns the same data type as the numeric data type of the argument.
When you need a value from the first or last row of a sorted group, but the needed value is not the sort key, the FIRST and LAST functions eliminate the need for self-joins or views and enable better performance.
The aggregate_function argument is any one of the MIN, MAX, SUM, AVG, COUNT, VARIANCE, or STDDEV functions. It operates on values from the rows that rank either FIRST or LAST. If only one row ranks as FIRST or LAST, then the aggregate operates on a singleton (nonaggregate) set.
The KEEP keyword is for semantic clarity. It qualifies aggregate_function, indicating that only the FIRST or LAST values of aggregate_function will be returned.
DENSE_RANK FIRST or DENSE_RANK LAST indicates that Oracle Database will aggregate over only those rows with the minimum (FIRST) or the maximum (LAST) dense rank (also called olympic rank).
See Also:
Table 3-10, "Implicit Type Conversion Matrix" for more information on implicit conversion and LASTAggregate Example
The following example returns, within each department of the sample table hr.employees, the minimum salary among the employees who make the lowest commission and the maximum salary among the employees who make the highest commission:
SELECT department_id,
MIN(salary) KEEP (DENSE_RANK FIRST ORDER BY commission_pct) "Worst",
MAX(salary) KEEP (DENSE_RANK LAST ORDER BY commission_pct) "Best"
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
ORDER BY department_id, "Worst", "Best";
DEPARTMENT_ID Worst Best
------------- ---------- ----------
10 4400 4400
20 6000 13000
30 2500 11000
40 6500 6500
50 2100 8200
60 4200 9000
70 10000 10000
80 6100 14000
90 17000 24000
100 6900 12000
110 8300 12000
7000 7000
Analytic Example
The next example makes the same calculation as the previous example but returns the result for each employee within the department:
SELECT last_name, department_id, salary,
MIN(salary) KEEP (DENSE_RANK FIRST ORDER BY commission_pct)
OVER (PARTITION BY department_id) "Worst",
MAX(salary) KEEP (DENSE_RANK LAST ORDER BY commission_pct)
OVER (PARTITION BY department_id) "Best"
FROM employees
ORDER BY department_id, salary;
LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID SALARY Worst Best
------------------- ------------- ---------- ---------- ----------
Whalen 10 4400 4400 4400
Fay 20 6000 6000 13000
Hartstein 20 13000 6000 13000
. . .
Gietz 110 8300 8300 12000
Higgins 110 12000 8300 12000
Grant 7000 7000 7000