| Oracle® Database Administrator's Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10595-04 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Administrator's Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10595-04 |
|
|
View PDF |
This section describes the issues you must consider when choosing to run your database in NOARCHIVELOG or ARCHIVELOG mode, and contains these topics:
The choice of whether to enable the archiving of filled groups of redo log files depends on the availability and reliability requirements of the application running on the database. If you cannot afford to lose any data in your database in the event of a disk failure, use ARCHIVELOG mode. The archiving of filled redo log files can require you to perform extra administrative operations.
When you run your database in NOARCHIVELOG mode, you disable the archiving of the redo log. The database control file indicates that filled groups are not required to be archived. Therefore, when a filled group becomes inactive after a log switch, the group is available for reuse by LGWR.
NOARCHIVELOG mode protects a database from instance failure but not from media failure. Only the most recent changes made to the database, which are stored in the online redo log groups, are available for instance recovery. If a media failure occurs while the database is in NOARCHIVELOG mode, you can only restore the database to the point of the most recent full database backup. You cannot recover transactions subsequent to that backup.
In NOARCHIVELOG mode you cannot perform online tablespace backups, nor can you use online tablespace backups taken earlier while the database was in ARCHIVELOG mode. To restore a database operating in NOARCHIVELOG mode, you can use only whole database backups taken while the database is closed. Therefore, if you decide to operate a database in NOARCHIVELOG mode, take whole database backups at regular, frequent intervals.
When you run a database in ARCHIVELOG mode, you enable the archiving of the redo log. The database control file indicates that a group of filled redo log files cannot be reused by LGWR until the group is archived. A filled group becomes available for archiving immediately after a redo log switch occurs.
The archiving of filled groups has these advantages:
A database backup, together with online and archived redo log files, guarantees that you can recover all committed transactions in the event of an operating system or disk failure.
If you keep an archived log, you can use a backup taken while the database is open and in normal system use.
You can keep a standby database current with its original database by continuously applying the original archived redo logs to the standby.
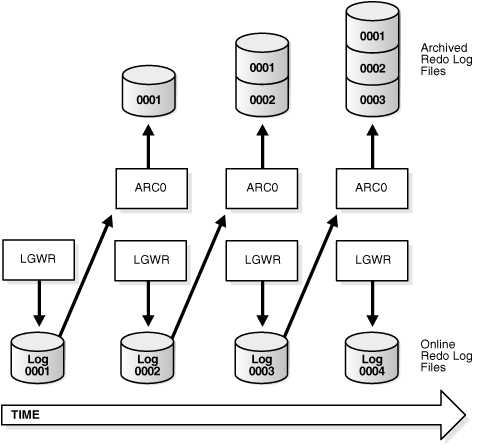
You can configure an instance to archive filled redo log files automatically, or you can archive manually. For convenience and efficiency, automatic archiving is usually best. Figure 12-1 illustrates how the archiver process (ARC0 in this illustration) writes filled redo log files to the database archived redo log.
If all databases in a distributed database operate in ARCHIVELOG mode, you can perform coordinated distributed database recovery. However, if any database in a distributed database is in NOARCHIVELOG mode, recovery of a global distributed database (to make all databases consistent) is limited by the last full backup of any database operating in NOARCHIVELOG mode.
Figure 12-1 Redo Log File Use in ARCHIVELOG Mode
Tip:
It is good practice to move archived redo log files and corresponding database backups from the local disk to permanent offline storage media such as tape. A primary value of archived logs is database recovery, so you want to ensure that these logs are safe should disaster strike your primary database.