| Oracle® Database Advanced Replication 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10706-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Advanced Replication 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10706-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter introduces deployment templates and describes how to use them to easily and efficiently distribute materialized view environments.
This chapter contains these topics:
Note:
Read Chapter 3, "Materialized View Concepts and Architecture" before you create a deployment template. Understanding materialized views better prepares you to build deployment templates.Oracle deployment templates provide you with the tools to efficiently deploy and administer a widely distributed materialized view environment. Before learning about the concepts, architecture, and use of deployment templates, consider the challenges of a mass deployment environment.
The need to have accurate information at any time and at any place continues to grow rapidly. At the same time, information is becoming decentralized and users are often disconnected from the network, requiring the information to be distributed to the active points-of-usage.
Consider the mobile sales force. Potentially hundreds, if not thousands, of professionals need accurate information about their customers on a laptop in a manner that causes the salesperson very little inconvenience. The challenge, therefore, is for the database administrator to roll out the data and the database infrastructure (tables, indexes, constraints, triggers, and so on) to all sites in an efficient and timely manner.
Traditionally, DBAs have been required to develop a deployment method of their own. Typically, the DBA was responsible for developing a very complex script to create the materialized view environment at the remote materialized view site. In addition to building the script, the DBA was often forced to customize data sets at the materialized view site. After the DBA completed engineering the script, deploying the script required manual packaging and implementation, both of which often required extensive troubleshooting.
The problems encountered in the preceding scenario have spawned technologies and resources dedicated to the art of efficient mass deployment. Mass deployment is the term used to describe the process of distributing database infrastructure, data, and front-end applications to a large number of users. For the purposes of Advanced Replication, the discussion of mass deployment is limited to the delivery of data and data infrastructure.
Mass deployment tools and technologies should aid the database administrator in delivering the data and database infrastructure. The goal is to define the environment once and create as many instances of the deployment template as necessary, while still maintaining the ability to customize individual sites.
To support this goal, Oracle's deployment templates enable you accomplish the following objectives:
Define the materialized view environment once
You define the structure of a materialized view environment once using a deployment template so that each user (site) receives the database infrastructure to support the front-end application.
Customize materialized view sites individually
You use deployment template parameters to customize each materialized view environment so that each user receives the particular data subset needed.
Mass deployment has many applications, such as distributing information to mobile sales forces, field technicians, retail stores, remote inventory collection sites, and so on. Such environments use deployment templates to build the database infrastructure at the remote site, largely because deployment templates support data subsetting, disconnected replication, and lower resource requirements, making them ideal for laptop users.
Oracle offers deployment templates to allow the database administrator to package a materialized view environment for easy, custom, and secure deployment. Packaging a deployment template is the process of defining the materialized view environment that will be created by the deployment template. Packaging a deployment template prepares it for instantiation at the remote materialized view site. Instantiation creates the materialized view site objects and populates the materialized views with data.
A deployment template can be as simple as a single materialized view with a fixed data set, or as complex as hundreds of materialized views with a dynamic data set based on one or more variables. Deployment template features include the following:
Centralized control
Ability to repeatedly deploy a materialized view environment
Template parameters that allow data subsetting or customization at remote site
Authorized user lists to control template instantiation and data access
To prepare a materialized view environment for deployment, create a deployment template at the master site. This template stores all of the information needed to deploy a materialized view environment, including the data definition language (DDL) to create the objects at the remote site and the target refresh group. This template also maintains links to user security information and template parameters for custom materialized view creation.
This section contains these topics:
Each deployment template contains the "blueprint" for creating the necessary materialized views and related objects at a materialized view site. Specifically, you create the deployment template at the master site, adding the necessary materialized views, triggers, views, and so on to the template as needed to create the materialized view environment. You can optionally define template parameters and authorized users, giving the template greater flexibility and security during the instantiation process.
Deployment template elements can be divided into the following four categories:
Oracle deployment templates center around the general template information, which consists of the template name, target refresh group, and private/public status. As illustrated in Figure 4-1, the REFRESH_TEMPLATE_NAME is used in all aspects of deployment template data dictionary views. You add the materialized view environment objects to the template prior to releasing the template for distribution according to the specified template identification (see Figure 4-2).
A deployment template is defined at a single master site. While you cannot have two deployment templates at the master site with the same name, you can copy a deployment template to another site using the same deployment template name.
Figure 4-1 Deployment Template View Relationships
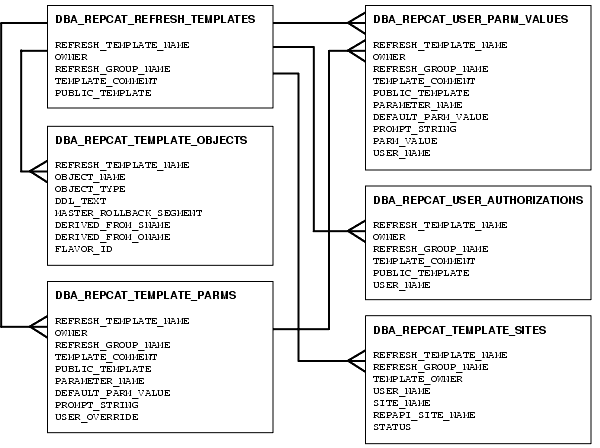
Figure 4-2 Deployment Template Elements Added to Template
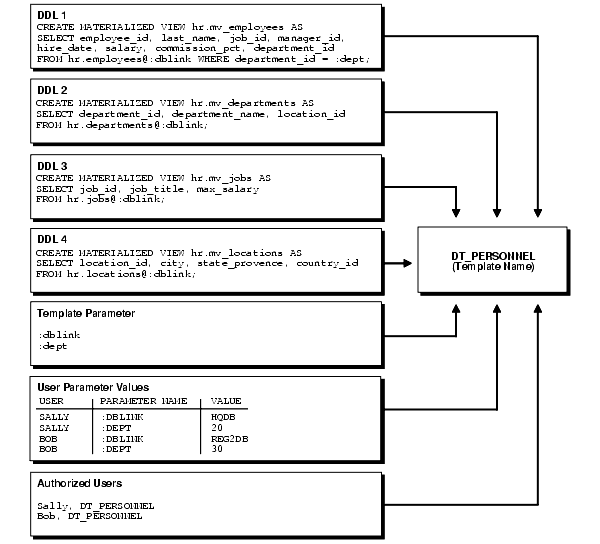
After the template has been defined, add objects to the template. When the template is instantiated at the materialized view site, the object DDL (that is, CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW, CREATE TABLE, and so on) is executed to create the appropriate objects at the materialized view site.
You can add objects to a deployment template that are based on a existing master objects, but if necessary, you can create a new template object by defining DDL to create the object. Oracle checks any new object DDL to ensure that it is lexically correct, which prevents the execution of faulty DDL. Updatable materialized views added to a deployment template must be based on a table in a master group, but other objects, such as read-only materialized views, can be based on objects that are not in master groups.
In most cases, you add materialized views to the template, but if necessary, you can add other objects. For example, constraints can be added to enforce data integrity at the materialized view site, views can be added for displaying data, or tables can be added for local data storage. In some cases, you might even include all objects for an application in a deployment template. Materialized views created using a deployment template are automatically added to the refresh group defined for the template.
You cannot use deployment templates to instantiate the following types of objects:
User-defined types
User-defined type bodies
User-defined operators
Indextypes
Nor can you use deployment templates to instantiate any objects based on these types of objects.
See Also:
"General Template Information" for more information about the refresh groupIf each target materialized view site requires a data set unique to its site, then you can define variables in the object DDL. These variables create a parameterized template that allows for custom data sets when the template is instantiated, allowing different materialized view sites to have different data sets. These parameters are embedded in the object DDL. During template instantiation, the individual user values for these parameters are substituted.
Oracle enables you to specify default values and user-specific parameter values for a template. You can enter the parameter values during the creation of the deployment template or after the template is created, but you must enter the parameter values before the template is instantiated. Users cannot enter values for parameters during instantiation.
If user-specific parameter values exist, then these values are automatically used when the specified user instantiates the template. For example, consider the variable region. Suppose you establish the following user-specific parameter values for template sales_temp:
| User | Region |
|---|---|
| fay | east |
| baer | west |
The defining SELECT statement for the materialized view is the following:
SELECT cust_id, sales_to_date, status FROM table_x WHERE region_id=:region;
When users fay and baer instantiate template sales_temp, their resulting materialized view data sets are the following:
| User fay | - | User baer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cust_id | region | - | cust_id | region |
| a123 | east | - | b123 | west |
| a234 | east | - | b234 | west |
| a345 | east | - | b345 | west |
| a456 | east | - | b456 | west |
In addition to creating customized data subsets, you can use template parameters in the WHERE clause of a CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW statement to securely limit the materialized view site to viewing and changing only the data that satisfies the WHERE clause. For example, suppose you have specified the following for the region parameter in the user specific parameters list:
| User | Region |
|---|---|
| fay | east |
| baer | west |
Users accessing the materialized view instantiated by user fay only see data for region east and can only view, update, or delete data that complies with this WHERE clause. In other words, a user of this materialized view cannot view, update, or delete data for region west, because the materialized view only contains data for region east.
Deployment templates can be either public or private. You set this when you create the template. If a template is public, then any user with access to the master site can instantiate the template.
If a template has been created for private use, then only authorized users can instantiate the target template. To enforce private use, create a list of authorized users at the master site. If an unauthorized user attempts to instantiate the target template, then the instantiation process fails.
Maintaining the emphasis on centralized control, you can monitor and manage certain characteristics of the instantiated environment at the remote materialized view site. Specifically, you have the ability to view the sites that have instantiated a deployment template, which includes the deployment template name, authorized user, and status of the instantiated environment.
When you have completed defining your deployment template, the template must be packaged to prepare it for instantiation at the remote materialized view site. When the packaged deployment template is instantiated at a materialized view site, the materialized view site objects are created and the materialized views are populated with data. Remote materialized view sites can be created either through online or offline instantiation.
Online instantiation allows a materialized view site to instantiate a deployment template while connected to the target master site. During the online instantiation process, the structure of the materialized view site is created, and the specified data subset is pulled from the master site and stored in the appropriate materialized views.
Packaging a deployment template for online instantiation means generating a script file that, when run at the materialized view site, creates the materialized view objects and connects to the master site to populate the materialized views with data. SQL statements such as CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW ... AS SELECT are used to populate the materialized views with data over a network from the master site.
One of the benefits of online instantiation is that the data subset is current as of the instantiation process. This data currency, however, comes at a cost. Online instantiation requires a "live" connection between the materialized view and master sites, which, depending on the size of the materialized view environment created, might increase network traffic.
Furthermore, laptop users connected by a modem might need to stay connected for a long time. The duration of the connection depends on the number of objects created, the complexity of the materialized view subqueries, and the amount of data transmitted, especially over low bandwidth modem lines.
To decrease server loads during peak usage periods and reduce remote connection times, you can choose offline instantiation of the template for your environment. Packaging a template for offline instantiation means generating a script or a binary file that contains the DDL and data manipulation language (DML) to build the materialized view environment defined in the deployment template and populate the environment with data. You package the script or binary file and save the file to some type of storage media (such as tape, CD-ROM, and so on), and then provide a means of transferring the script or binary file to the materialized view site. Each materialized view site requires a separate offline instantiation script.
When you package a template for instantiation, the materialized view logs for each master table on which a materialized view is based in the template begin to log changes. The materialized view log for a particular master table does not clear these changes until every materialized view based on the master table refreshes after instantiation. Therefore, to prevent the materialized view log from growing large, the template should be instantiated, and the materialized views should be refreshed as soon as possible after packaging.
During instantiation, the template and data are pulled from the storage media, instead of being pulled from the master site. This operation has the benefit of reducing network traffic and eliminating the need for a constant network connection. However, after instantiation, the data in the materialized view site reflects the master site data at packaging time and must be made current by a refresh.
Offline instantiation is an ideal solution for mass deployment situations where many laptops and other disconnected computers are instantiating the target template.
When you use deployment templates to create a materialized view site using offline instantiation, the conflict resolution methods defined on the master tables are not pulled down to the materialized view site. These conflict resolution methods might be required to ensure data consistency if you plan to create materialized views based on this materialized view site (multitier materialized views). If you use online instantiation, then the conflict resolution methods are pulled down during instantiation.
Table 4-1 summarizes the scenarios for instantiating of a deployment template.
Table 4-1 Scenarios for Instantiating a Deployment Template
| Type of Instantiation | Description |
|---|---|
|
Offline |
The user runs the offline instantiation script with SQL*Plus. The offline instantiation script contains both |
|
Online |
The user runs the online instantiation script with SQL*Plus. The online instantiation script contains |
Either you (the DBA) or the target user can package the deployment template. Either use the Advanced Replication interface's Create Deployment Template Wizard to package a template for offline instantiation, or the replication management API to package a template for offline or online instantiation. End-users use the public API to package a deployment template, while DBAs generally use the private API for packaging.
Typically, when a deployment template will be instantiated offline, the DBA performs the packaging, but when the deployment template will be instantiated online, the user can perform the packaging. However, there are no restrictions on users or DBAs performing either online or offline packaging, other than the use of different API calls.
The following replication management API functions can be used to package a deployment template.
Private functions (DBA only):
DBMS_REPCAT_RGT.INSTANTIATE_OFFLINE function
DBMS_REPCAT_RGT.INSTANTIATE_ONLINE function
Public functions:
DBMS_REPCAT_INSTANTIATE.INSTANTIATE_OFFLINE function
DBMS_REPCAT_INSTANTIATE.INSTANTIATE_ONLINE function
Note:
When you package a deployment template for offline instantiation, the related materialized view logs begin logging for the materialized views that were packaged in the template. This immediate logging enables the remote materialized view site to perform a fast refresh after completing the offline instantiation process. Monitor the materialized view logs to ensure that remote materialized view sites refresh in a timely manner after performing an offline instantiation. Remote materialized view sites that have not refreshed cause the materialized view log to grow quite large, because logging begins when the template is packaged.See Also:
"Preparing Materialized View Sites for Instantiation of Deployment Templates", and see Oracle Database Advanced Replication Management API Reference for information about the functionsOracle uses standard materialized view architecture with deployment templates to distribute materialized view environments quickly and effectively. Deployment templates use the same methods in creating materialized view definitions, refresh characteristics, conflict resolution, and grouping as used when manually building a materialized view environment. The distinction to remember is that instead of executing the DDL to create the object immediately, the object DDL is simply contained in a deployment template and is executed when the template is instantiated.
This section contains these topics:
Instead of executing DDL at the materialized view site to immediately create a materialized view environment, the materialized view and other related object definitions are stored within the deployment template. After all of the object definitions have been added to the deployment template, the template can be instantiated to execute all of the stored DDL at the remote materialized view site, which creates the necessary materialized view environment.
All of these object definitions are stored in system tables maintained at the deployment template definition site, keyed on the deployment template name. When the deployment template is packaged, the stored object DDL is pulled from these system tables to create the instantiation script of binary file.
Template object definitions are created using the same DDL that is used to create the objects locally at the materialized view site. For example, you can issue the following statement to create a materialized view:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW hr.departments_mv
REFRESH FAST WITH PRIMARY KEY FOR UPDATE AS SELECT
department_id, department_name, manager_id, location_id
FROM hr.departments@orc1.example.com;
To add this same materialized view to a deployment template, you can use the Advanced Replication interface's Create Deployment Template Wizard, or execute the CREATE_TEMPLATE_OBJECT function, as shown in the following example:
DECLARE
tempstring VARCHAR2(3000);
a NUMBER;
BEGIN
tempstring := 'CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW hr.departments_mv
REFRESH FAST WITH PRIMARY KEY FOR UPDATE AS SELECT
department_id, department_name, manager_id, location_id
FROM hr.departments@orc1.example.com';
a := DBMS_REPCAT_RGT.CREATE_TEMPLATE_OBJECT (
refresh_template_name => 'hr_refg_dt',
object_name => 'departments_mv',
object_type => 'MATERIALIZED VIEW',
ddl_text => tempstring,
master_rollback_seg => 'rbs');
END;
/
Note:
Do not place a terminating semi-colon in the DDL statement inside the single quotation marks for theddl_text parameter.Executing the preceding function adds the materialized view definition to the deployment template named dt_mviewenv. When this particular materialized view is instantiated, the materialized view mview_test is created. In addition to creating materialized views, you can add table, trigger, procedure, index, and other object definitions to the deployment template.
Whenever you create a materialized view, always specify the schema name of the table owner in the query for the materialized view. In the preceding example, hr is specified as the owner of the employees table.
See Also:
DBMS_REPCAT_RGT.CREATE_TEMPLATE_OBJECT in the Oracle Database Advanced Replication Management API Reference for information about using this functionWhen a deployment template is packaged in preparation for remote materialized view site instantiation, the template is being prepared for online or offline instantiation. The instantiation procedure creates the remote materialized view environment and populates the environment with data.
When a deployment template is packaged for online instantiation, the resulting DDL that is required to create the remote materialized view environment is generated and all template parameter substitutions are performed. Where this generated DDL is stored depends on the type of materialized view client.
The online instantiation script is stored locally on the hard drive of the computer from which replication management API is executed to package the template. If this computer is not the materialized view site computer, then the online instantiation file must be transferred to the materialized view site for online instantiation.
When a deployment template is packaged for offline instantiation, the DDL that is required to create the remote materialized view environment and the DML that is required to populate the environment with the data are both stored in a generated file. Also, during packaging, all template parameter substitutions are performed.
When a template is packaged, a script or binary file is created for offline instantiation and is saved to a storage device, such as hard disk, CD-ROM, tape, and so on. Either the Advanced Replication interface's Create Deployment Template Wizard or the replication management API can be used to package a deployment template for offline instantiation.
The offline instantiation script is stored locally on the hard drive of the computer from which the request is made to package the template. If this computer is not the materialized view site computer, then the offline instantiation file must be transferred to the materialized view site for offline instantiation.
When the remote materialized view site instantiates the template, the script or binary file is executed from the storage media or from the local hard drive. This execution creates the materialized view environment and populates the environment according to the data set defined during the packaging process. Recall that any template parameters that define the data set for individual sites are defined during the packaging process.
During the online instantiation process, the structure of the materialized view site is created, and the specified data subset is pulled from the master site and stored in the appropriate materialized views. Also, after the remote materialized view site begins the online instantiation process, Oracle evaluates the parameters that have been defined for the deployment template. Any values defined for these parameters are used when the object DDL in the template is executed so that custom data sets can be installed at the remote materialized view site. At the same time, the materialized views are registered at the master site, and the materialized view logs begin logging the changes to the master tables.
Two possible methods can be used to define template parameter values: default parameter values and user parameter values. Oracle checks to see if these parameter values exist and then uses them according to the hierarchy:
User Parameter Values
Default Parameter Values
If user parameter values have been defined and a listed user is instantiating the template, then the user parameter values are used when instantiating the template. If no user parameter values have been defined, then Oracle uses the default parameter values. Figure 4-5 shows the parameter checking process.
Figure 4-5 Checking for Parameters During Online Instantiation
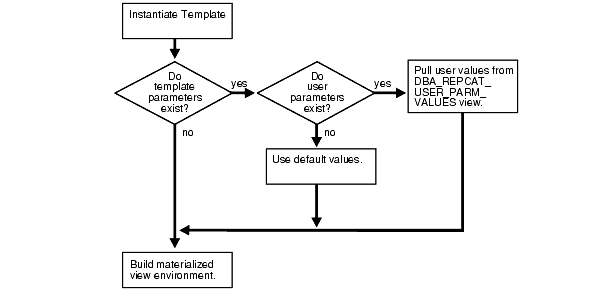
After the parameters are checked, the objects created by the template are added to the refresh group specified when the template was created.
In a mass deployment environment, most materialized view environments use the offline instantiation method to create the necessary materialized view environment. When you package the deployment template, a script or binary file is created to store the DDL needed to create the materialized view environment, the parameter values used during the instantiation process, and the DML necessary to populate the materialized view environment with data.
The script or binary file can be copied to a CD-ROM, floppy disk, or other storage media or can be posted on a Web or FTP site to be downloaded to the remote materialized view site. It can also be transferred using the DBMS_FILE_TRANSFER package. The flexibility in delivery mechanisms allows you and your users to choose the most effective method for instantiating a deployment template.
A number of possibilities for deployment template packaging and instantiation are available. Table 4-2 illustrates the possibilities, identifies the mechanism for packaging and instantiation, and lists the documentation to use when you perform an operation.
Table 4-2 Packaging and Instantiation Options
| Type of Instantiation | Package Template Using | Packaging Documentation | Instantiate Template Using | Instantiating Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Offline |
Advanced Replication interface Create Deployment Template Wizard |
See the Advanced Replication interface's online Help. |
Offline Instantiation Script and SQL*Plus |
See the Advanced Replication interface's online Help. |
|
Offline |
The Replication Management API (PL/SQL Packages and SQL*Plus) |
See the instructions for packaging in Oracle Database Advanced Replication Management API Reference. |
Offline Instantiation Script and SQL*Plus |
See the instructions for instantiating a deployment template in Oracle Database Advanced Replication Management API Reference. |
|
Online |
The Replication Management API (PL/SQL Packages and SQL*Plus) |
See the instructions for packaging in Oracle Database Advanced Replication Management API Reference. |
Online Instantiation Script and SQL*Plus |
See the instructions for instantiating a deployment template in Oracle Database Advanced Replication Management API Reference. |
After instantiating a deployment template at a remote materialized view site, the structure created is exactly the same as if you had created the materialized view environment locally at the materialized view site. Specifically, Oracle creates the materialized view, with the specified name, and an index based on the primary key to maintain constraint consistency. Other objects in the template are also created as if they were created manually at the materialized view site.
With respect to offline instantiations, the longer the duration between the packaging at the server and the instantiation at the remote site, the longer it takes for the first refresh after instantiation at the remote materialized view site. The materialized view site uses the materialized view log at the master site to perform the fast refresh from the time that the template was packaged. Recall that changes made to the master table are logged to the materialized view log as soon as you package the deployment template.
See Also:
"Materialized View Architecture" for more informationObjects created by an instantiated deployment template are added automatically to a materialized view group with the same name as the object's master group. For example, if you instantiated the dt_mviewenv deployment template, which contains objects from the personnel and technical master groups, then your template objects are added to materialized view groups personnel and technical, respectively. Remember that a materialized view group helps to maintain organizational consistency with the target master group and, more importantly, is required for updatable materialized views.
See Also:
"Materialized View Groups" for more informationWhen you first begin building a deployment template, you define the name of the refresh group to which the template's materialized view objects will be added. After the instantiation process is finished, you can specify that the materialized views in the refresh group be refreshed automatically at set intervals, assuming a constant network connection to the master site.
You can use the Advanced Replication interface in Oracle Enterprise Manager, or DBMS_REFRESH.CHANGE procedure, to change the refresh interval and next refresh data of a refresh group. To change these settings in the Advanced Replication interface, select the refresh group and edit the Next Date and Interval fields. To change these settings with the DBMS_REFRESH.CHANGE procedure, set the interval and next_date parameters appropriately. If materialized view sites do not have a constant network connection to the master site, then they can refresh their refresh groups on-demand.
The following are examples of simple date expressions that you can use to specify next_date and interval:
A next_date or interval of one hour is specifies as:
SYSDATE + 1/24
A next_date or interval of seven days is specifies as:
SYSDATE + 7
See Also:
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide and Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information about date arithmeticThe combination of deployment template parameters and subquery subsetting gives the database administrator a powerful tool to administer a widely distributed database environment using subqueries and row-subsetted data. Additional design consideration must be given to column subsetting requirements and data sets needed for a replication environment.
Materialized view data sets are defined based on the materialized view's query, meaning that the user only sees data that complies with the materialized view's defining query. Both row and column subsetting enable you to create materialized views that contain customized data sets. Such materialized views can be helpful for regional offices or sales forces that do not require the complete corporate data set.
This section contains these topics:
See Also:
"Data Subsetting with Materialized Views" for more information about data subsettingColumn subsetting enables you to exclude columns that are in master tables from materialized views. You do this by specifying certain select columns in the SELECT statement during materialized view creation. Column subsetting is only possible through the use of deployment templates. Before you begin assembling your deployment template, consider how to build your templates.
For example, in a mass deployment environment with many "lightweight" clients, you might need to replicate tables that contain LOB data without actually replicating the LOB data itself. This goal can be achieved by excluding the LOB column from the selected columns to be replicated when defining the column subset.
You can select any subset of columns in a read-only materialized view. For an updatable materialized view, the subset of columns must contain the following columns:
Primary key column(s)
All columns used for conflict resolution for the replicated columns (see Figure 4-6)
Note:
While it is possible to configure column subsetting within a column group, it is not recommended because it can result in data inconsistencies between sites. When using column subsetting, you should eliminate columns at the column group level.Figure 4-6 Replicate Column-Subsetted Data
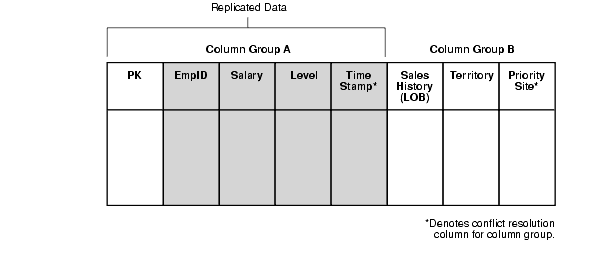
If you are adding a materialized view that replicates columns pk, empid, salary, and level (illustrated in Figure 4-6), then you also need to include the Time Stamp column because it is used for conflict resolution for columns contained in Column Group A.
Note:
Column subsetting is only available when you add a materialized view to a deployment template using the Advanced Replication interface in Oracle Enterprise Manager. Column subsetting is not available when using the replication management API.
The master definition site must be available when defining a column subset. If your deployment template contains column-subsetted materialized views from multiple master groups, then the master definition site for each group must be available.
Row subsetting enables you to exclude rows that are in master tables from materialized views by using a WHERE clause. For example, the following statement creates a materialized view based on the oe.orders@orc1.example.com master table and includes only the rows for the sales representative with a sales_rep_id number of 173:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW oe.orders REFRESH FAST FOR UPDATE AS SELECT * FROM oe.orders@orc1.example.com WHERE sales_rep_id = 173;
Rows of the orders table with a sales_rep_id number other than 173 are excluded from this materialized view.
In some situations, you can benefit from using row subsetting with an assignment table. An assignment table lets you relate one entity to another entity in your database, without storing the assignment information in either of the tables for the two entities. This technique is best illustrated through an example.
In the oe schema, the product_id column is the primary key in the product_information table, and the warehouse_id column is the primary key in the warehouses table. In this schema, the inventories table functions as an assignment table because it assigns a product to a warehouse using the product_id column and the warehouse_id column. These two columns form the primary key of the inventories table.
With these three tables in oe schema (inventories, product_information, and warehouses), you can track which products are in which warehouses without storing the product_id information in the warehouses table, nor the warehouse_id information in the product_information table. To illustrate why this is important, consider what would happen if the inventories table did not exist and the warehouse_id column was a foreign key in the product_information table.
In this case, if a salesperson wants to store product information for the nearest warehouse, then the sales person would need to specify the warehouse_id for the warehouse in the WHERE clause of the CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW statement. For example, the salesperson might create the materialized view using the following statement:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW oe.product_information REFRESH FAST FOR UPDATE AS SELECT * FROM oe.product_information@orc1.example.com WHERE warehouse_id = 1;
The drawback to this configuration is that the warehouse_id is "hard coded" into the materialized view definition. If the company closes warehouse 1 or opens a new warehouse that is even closer to the salesperson, then the preceding materialized view definitions would need to be altered or re-created. With this in mind, if you use assignment tables in conjunction with row subsetting in a subquery, then you can easily control changes to a materialized view environment.
In the oe schema, the warehouse_id column is not part of the product_information table. Instead, a product is assigned to a warehouse through the inventories table. This relationship between products and warehouses is illustrated in Figure 4-7.
Figure 4-7 Product/Warehouse Relationship
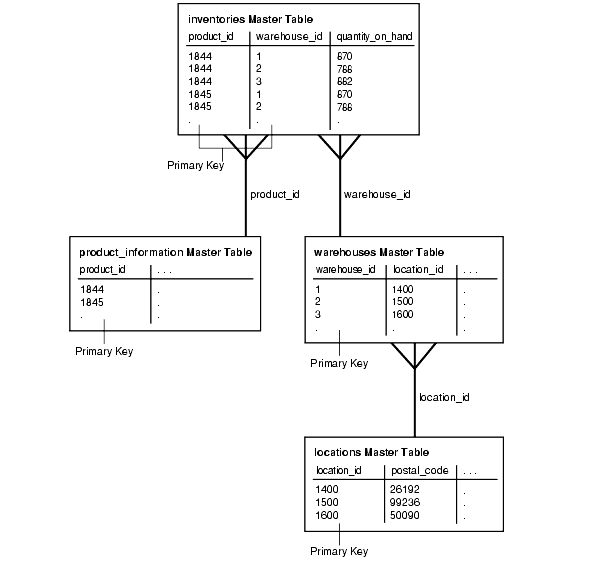
If new warehouses are built or other warehouses are closed, then you can use the inventories table to assign products to different warehouses. Besides creating a single point of administration, assignment tables, such as the inventories table, used in conjunction with row subsetting in subqueries, can ensure security. For example, if necessary, you can limit a certain salesperson to see data for some warehouses but not others.
If we assume that each salesperson is responsible for a particular location and only requires product information for products that are stored in a warehouse in that location, then we can use the inventories table as an assignment table along with row subsetting in subqueries to create the product_information materialized view that contains only the relevant information for a particular salesperson. The following statement provides a salesperson with the proper data:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW oe.product_information REFRESH FAST FOR UPDATE AS
SELECT * FROM oe.product_information@orc1.example.com pi
WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM oe.inventories@orc1.example.com inv
WHERE pi.product_id = inv.product_id
AND EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM oe.warehouses@orc1.example.com w
WHERE inv.warehouse_id = w.warehouse_id
AND EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM hr.locations@orc1.example.com loc
WHERE w.location_id = loc.location_id
AND loc.postal_code = :p_code)));
Note:
To create thisoe.product_information materialized view, postal_code in must be logged in the materialized view log for the hr.locations table. See "Logging Columns in the Materialized View Log" for more information.The product_information materialized view is populated with product information for the products that are stored in the warehouse located at the postal code specified with the p_code variable. Notice the p_code variable in the last line of the CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW statement.
With this flexibility, managers can easily control materialized view data sets by making simple changes to the inventories table, without requiring modification of the SQL for the materialized view creation statements. For example, if a new product is added to a particular warehouse, then the manager would simply add a row to the inventories table that assigns the product to the warehouse. After the next materialized view refresh, the data for the product is added to the materialized view site that tracks product information for the warehouse.
When designing your deployment templates, consider the different sets of users that need to access the target data. For example, both salespersons and technicians need customer information, but the technicians might not need sales information. You do not want users to instantiate deployment templates that contain extraneous data, because it requires extra storage space and incurs longer refresh time.
On the other hand, if you have users that require both sales and customer support information, then you do not want users to have to instantiate multiple deployment templates that share redundant data. Instantiating multiple templates might cause data consistency problems. Each deployment template uses a different refresh group, which means that data in the two deployment templates can be refreshed at different times, possibly causing data consistency problems.
In this case, the best solution would be to have one deployment template for salespersons, one for customer service technicians, and one for users that require both sets of data.
To save time and effort, the best way to create these three templates is to create the template with both sets of data first, copy the template twice, deleting unneeded items to create the other deployment templates.
Figure 4-8 The Different Needs of Salespersons and Customer Support Technicians
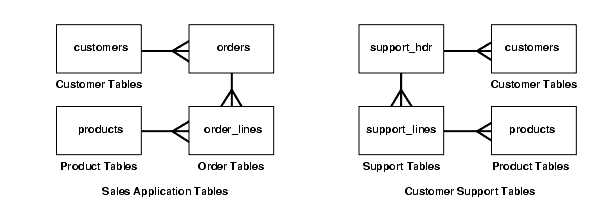
Another design consideration is the usage of parameters. If many of the tables in Figure 4-8 use the customer_id field, then you could define the same parameter in each of the template objects. By using the same parameter, you would only need to define the default parameter value once, and it would be used for all objects during the instantiation process.
Using a single template parameter is even more useful when used with materialized views that use subquery subsetting. One parameter allows a user to receive only the data for the customers that the user needs. Consider the following CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW statements:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW sales.orders AS
SELECT * FROM sales.orders@orc1.example.com o
-- conditions for customers
WHERE EXISTS
( SELECT c_id FROM sales.customer@orc1.example.com c
WHERE o.c_id = c.c_id
AND EXISTS
( SELECT * FROM sales.assignment@orc1.example.com a
WHERE a.c_id = c.c_id
AND EXISTS
( SELECT * FROM sales.salesperson@orc1.example.com s
WHERE s.s_id = :salesperson_id)));
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW sales.customer AS
SELECT c_id FROM sales.customer@orc1.example.com c
-- conditions for customers
WHERE EXISTS
( SELECT * FROM sales.assignment@orc1.example.com a
WHERE a.c_id = c.c_id
AND EXISTS
( SELECT * FROM sales.salesperson@orc1.example.com s
WHERE s.s_id = :salesperson_id)));
Even though the two materialized views being created do not explicitly contain the salesperson_id field, using subquery subsetting makes using parameters very effective for instantiating only required data sets. Using a single parameter (:salesperson_id) makes managing and instantiating these materialized views easier for both the DBA and the user instantiating the deployment template.
Finally, consider what other objects need to be created at the remote materialized view site. Consider the following questions:
Do you need to include the DDL to create the necessary database links from the materialized view site to the master site?
What triggers or procedures does the materialized view environment require?
Do any tables need to be created that store nonreplicated data?
Are any extra indexes required?
A deployment template is the most effective method of building and distributing a materialized view environment. Even if distribution is limited to only two or three sites, you still significantly reduce the amount of steps needed to build a materialized view environment by using deployment templates as opposed to individually creating the materialized view environment at those two or three sites. With deployment templates, you build once and distribute as needed.
However, one question remains: If a deployment template is the most effective means for building and distributing a materialized view environment, then when should you locally build the materialized view environment at the remote materialized view site? In most cases, you should build a materialized view environment using the Materialized View Group Wizard or locally at the materialized view site when local control must be maintained at the materialized view site.
One scenario where you might find local control of materialized view creation helpful is when it is desirable for the materialized view site to control what data it receives. For example, this is especially true of decision support sites (DSS), which are typically read-only materialized view sites. A DSS site might occasionally need to run complex queries and they do not want to slow the OLTP site, or bother the DBA at the OLTP site.
One of the major benefits of deployment templates is that control is maintained centrally by the DBA building the deployment template. In some cases, however, the materialized view site must retain some control.
Local control might be required if the materialized view site:
Has an experienced DBA
Is considered a trusted site
Is a materialized view instead of a master site because of row subsetting requirements
Because materialized view groups are created with the Advanced Replication interface's Create Materialized View Group Wizard locally at the materialized view site by its DBA, or perhaps a systems analyst with SQL knowledge, control can also be maintained at the materialized view site.
Consider the following as a perfect example for maintaining local control. Because multimaster replication does not allow for row and column data subsetting, updatable materialized view sites are sometimes created primarily for their ability to subset data. These sites are typically secure, have experienced DBAs, and require the ability to maintain control locally to meet user and application requirements. Materialized view groups created with the Materialized View Group Wizard or with the replication management API allow for the localized control necessary to meet the requirements of the secure updatable materialized view sites.
Also, remember that when a materialized view environment is created with a deployment template, all objects in the materialized view environment are added to the same refresh group. While this might be fine for most installations, certain situations might require that the objects in a materialized view group are assigned to several different refresh groups.