| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
A cursor variable points to the unnamed work area in which the database stores processing information when it runs a multiple-row query. With this pointer to the work area, you can access its information, and process the rows of the query individually.
To create a cursor variable, define a REF CURSOR type, and then declare the cursor variable to be of that type. Declaring a cursor variable creates a pointer, not an item. A cursor variable holds the address of an item instead of the item itself (like a C or Pascal pointer).
Topics:
Syntax
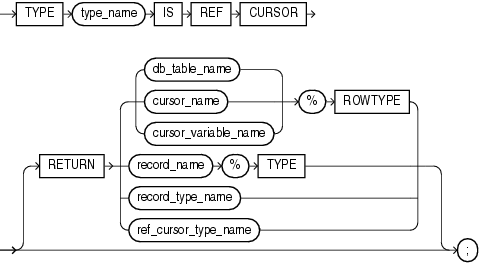
ref_cursor_type_definition ::=
cursor_variable_declaration ::=
Semantics
cursor_name
The name of an explicit cursor.
cursor_variable_name
The name of a cursor variable.
db_table_name
The name of a database table or view, which must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
record_name
The name of a user-defined record.
record_type_name
The name of a user-defined type that was defined with the data type specifier RECORD.
RETURN
Specifies the data type of the value that the cursor variable returns.
Specify RETURN to define a strong REF CURSOR type. Omit RETURN to define a weak REF CURSOR type. For information about strong and weak REF CURSOR types, see "Cursor Variable Creation".
%ROWTYPE
See "%ROWTYPE Attribute".
%TYPE
See "%TYPE Attribute".
type_name
The name of the REF CURSOR type that you are defining and the type of the cursor variable that you are declaring.
Usage
A REF CURSOR type definition can appear either in the declarative part of a block, subprogram, package specification, or package body (in which case it is local to the block, subprogram, or package) or in the "CREATE TYPE Statement" (in which case it is a standalone stored type).
A cursor variable declaration can appear only in the declarative part of a block, subprogram, or package body (not in a package specification).
Cursor variables are subject to the restrictions in "Cursor Variable Restrictions".
Examples
Related Topics
In this chapter:
In other chapters: